How to Optimize E-Commerce Product Pages for SEO
Stand Out from Your Competitors
As an e-commerce business owner, you know how important having a solid online presence is. But with so many competitors, it can be tough to stand out and attract customers to your website.
One effective way to improve your visibility and drive more traffic to your site is through search engine optimization (SEO). This post will guide you to optimize e-commerce product pages for SEO success.

Why Optimizing Product Pages is Tricky
In SEO, you can’t just look at product pages in isolation because search engines don’t view your store that way either. Pages affect one another (positively and negatively), so you need to look beyond product pages. Search engines evaluate your entire store; the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Optimizing product pages requires you to focus on these pages without losing sight of the bigger picture—how your product pages work together—or the rest of your site.
When it comes to the bigger picture, you have to deal with:
- Category pages and product pages compete for the same queries
- Very similar product variants
- Products available in multiple categories
- Discontinued or expired products
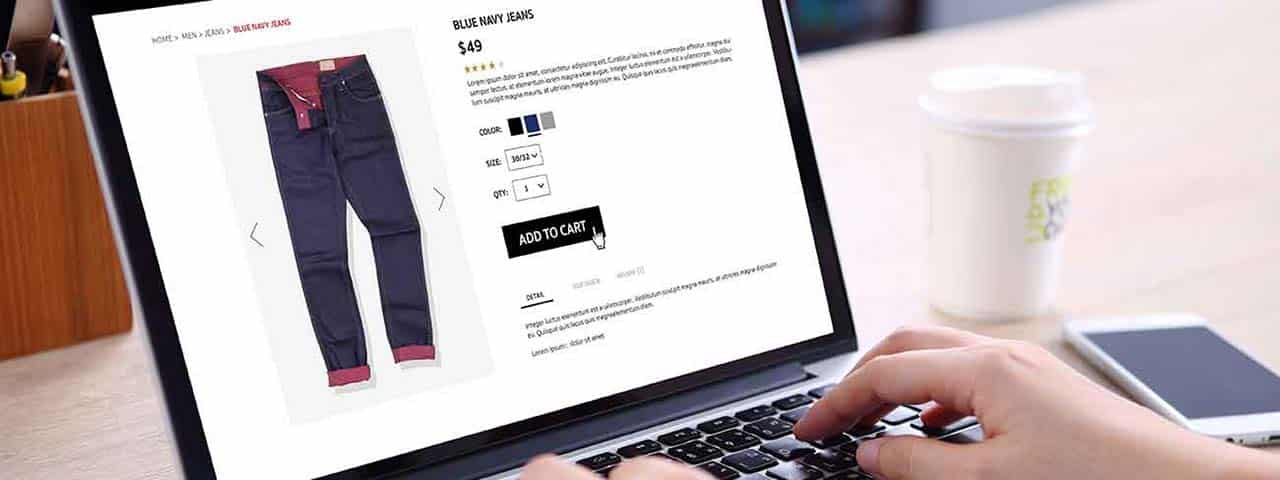
20 Tips to Optimize E-Commerce Product Pages for SEO
1. Do Keyword Research
Before you optimize your e-commerce product pages for SEO, you must understand what terms and phrases your potential customers use to search for products like yours. This need is where keyword research comes in.
Several tools are available to help you identify the most popular and relevant keywords, such as Google’s Keyword Planner and SEMrush. Once you have a list of keywords, you can use them to inform the content and structure of your product pages.
2. Align Product Names with Your Keyword Strategy
Aligning product names with your target search queries goes a long way. Include the brand name, product name, model number, and helpful product attributes such as color, size, and even the SKU if that makes sense.
Let’s say you run an e-commerce store selling backpacks and want to rank for Sakura Day Pack Women. You must include those keywords in your product name, meta information, and URL. We’ll cover the meta information and URL in detail below, but let’s first focus on the product name.
You don’t want product pages to compete with your category page, so you are for product-specific queries only, not for brand or brand + product category queries.
3. Write Descriptive and Consistent Product URLs
A good URL structure helps visitors and search engines understand your site structure. And you’re likely to get more clicks on your snippet in Google when the visitor sees a URL that reflects their search query.
A good URL structure is descriptive, easy to read, consistent, brief, and lowercase.
Regarding product pages, the last part of the URL—the so-called URL slug—is relevant.
In the case of the Sakura Day Pack Women’s page, a great URL slug would be sakura-day-pack-women, making the full URL, for example:
https://example.com/backpacks/hiking/sakura-day-pack-womens/
4. Include Meta Information in the Title Tag and Meta Description
When we talk about “meta information” within SEO, we’re referring to both the title tag and the meta description. Both are essential in how well your product page ranks and how it’s presented to searchers.
In addition to your product descriptions, there are a couple of other critical elements of your product pages that you need to optimize for SEO.
The first is the page title, the blue link appearing in search engine results. Your page title should include your primary target keyword and accurately reflect the page’s content.
A good title is:
- easy to read
- has important keywords at the start
- is unique
- has a length between 285 and 575 pixels
- (30 and 60 characters, respectively).
The second is the meta description, the short snippet of text that appears beneath the page title in search results. Your meta description should also include your target keywords and provide a compelling reason for users to click on your link.
A good meta description should also include your primary target keyword —except that the preferred length is from 430 to 920 pixels (70 and 155 characters, respectively), and we recommend including a call-to-action.
Especially for larger stores, it’s impossible to define titles and meta descriptions for every product manually. Therefore, we recommend working with templates to generate them automatically. You should be able to overwrite the automatically generated titles and meta descriptions manually.
That way, you can generate decent titles and meta descriptions in the blink of an eye, yet you can always go in and tweak them to perfection.
Here is an example template:
- Title tag: $productName – $storeName, which translates to Sakura Day Pack Women’s – Mont-Bell
- Meta description: Go on an adventure with the $productName. Order now for $productPrice—free shipping and next-day delivery! Which translates to Go on an adventure with the Sakura Day Pack Women’s. Order now for $175—free shipping and next-day delivery!
5. Write Descriptive Headings
Headings help visitors and search engines quickly see what a page is about and how it’s structured.
We recommend using the H1 heading for the product name. Then, use H2 headings for the most important sections, such as the product’s features, technical specifications, reviews, and Q&As. You can try to weave the product name into one of the H2s naturally, but if you’re finding that it hurts the user experience, don’t do it.
For our example, this would result in:
- H1: Sakura Day Pack Women
- H2s:
- Features
- Technical Specifications
- Reviews or Reviews for Sakura Day Pack Women
- Questions and Answers
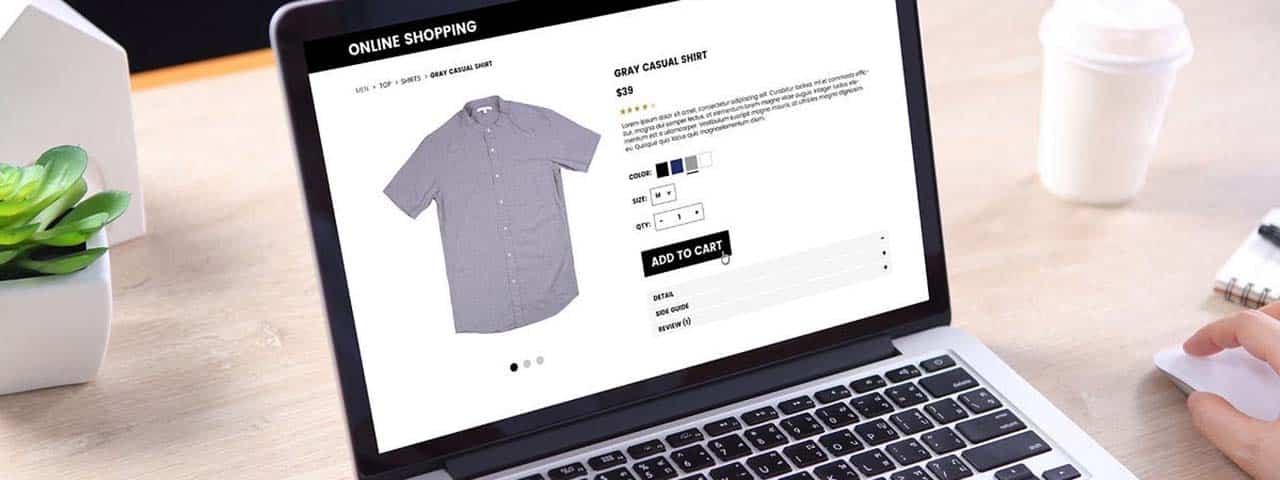
6. Include Product Attributes
Including product attributes helps you to rank for queries around the product. Include the brand name, series name, model name, and SKU.
Linking these product attributes is also a great way to strengthen your internal link structure.
Some examples to get you going:
- Link the brand name to the brand overview page.
- Link the series to the product series overview page.
- Link the gender to which the backpack is marketed to an overview of similarly sold backpacks.
- Link the gear capacity to the range the backpack is in, for example, 30–40L.
7. Create High-quality Product Descriptions
The product description is one of the most essential elements of an e-commerce product page. It is where you can provide potential customers with detailed information about the features and benefits of your product.
But it’s not enough to list the product’s specifications – your product descriptions must be unique, engaging, and informative. They should also include your target keywords, where appropriate, to signal to search engines what your page is about.
Solid product descriptions convince visitors to buy from you. Make them personal and engaging, and explain the product’s benefits and features, but don’t write an essay—nobody will read it.
You can also incorporate closely related, low-competition queries you want to rank for in your product description. But here again, don’t overdo it.
Cover the essential features first. For example, with the Sakura day pack Women’s, you could highlight the following:
- What the backpack is best used for
- Whether a rain cover is included
- What the backpack’s capacity is
- Whether the backpack is reservoir (“hydration bladder”) compatible
Besides describing the product, we also highly recommend listing its specifications such as size, color, and weight—everything a visitor may be searching for in Google and needing so they can make a purchase.

8. Use Images and Videos to Enhance Your Product Pages
In addition to text, your product pages should include high-quality product images and videos showcasing your products in action. These can help to increase user engagement and improve the overall user experience.
They can also provide additional opportunities to include your target keywords through image alt text, video titles, and descriptions.
Including high-quality product images showing the products in detail and context will likely improve conversion rates. Staying within the hiking theme: You need to show a person with the hiking gear, ideally in a natural environment.
Conversion rates aside, optimized images also improve your product page’s SEO performance.
The best practices here are to:
- Include product names in image file names and alt attributes.
- Serve the images in the correct format—it’s best to serve product images as JPGs or the popular new WebP format.
- Serve the images at the right size.
- Compress the images to decrease their file size.
- Include the images in an image XML sitemap.
- Ensure the images load fast and don’t slow down the overall page load.
9. Implement Internal and External Linking
In addition to optimizing your product pages, you can improve their SEO performance by implementing internal and external linking. Internal linking refers to other website pages like your homepage or category pages.
Internal linking can help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your site and improve the visibility of your product pages. External linking, on the other hand, refers to linking to other websites that are relevant and trustworthy. External links can help to improve the authority and credibility of your product pages in the eyes of search engines.
10. Include Breadcrumb Navigation
Good breadcrumb navigation works well for both visitors and search engines. Users can quickly grasp the store’s hierarchy and jump up to a category page using the breadcrumbs, and they add relevant internal links for search engines. But there are different views on how to structure them.
Important: Be sure to mark up your breadcrumbs with Schema to clarify what the breadcrumbs are and how machines should interpret them.

11. Improve Page Load Speed
Fast-loading stores make more money. Almost 70% of consumers say page speed impacts their willingness to buy from an online retailer.
A site that loads in 1 second has a conversion rate 5x higher than one that loads in 10 seconds—a 1-second reduction in load time results in a conversion rate increase of 5.6%.
When an e-commerce page loads slowly:
- Almost 50% of shoppers say they’ll try to refresh the page at least once.
- 22% of shoppers say they’ll close the tab.
- 14% say they’ll visit a competitor’s site.
In 2017, a Google study showed that as page load time goes from one second to 10 seconds, the probability of a mobile site visitor bouncing increases by 123%.
While page speed has long been a ranking factor for Google, with the rollout of the Page Experience Update and the introduction of Core Web Vitals, page load time has become even more critical.
Optimizing for speed is a technical endeavor, and you can tweak hundreds of tiny things to squeeze every millisecond out of your pages. But in practice, focusing on these three best practices will usually get you 90% of the way there:
1. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Instead of hosting your store in a single place, your content loads from a worldwide network of servers. When somebody visits your store, they connect to the endpoint closest to their location, decreasing the latency to reach your store. Plus, CDNs can cache your pages so they load blazingly fast.
2. Optimize your assets: Examples of assets are images, JavaScript code, and CSS stylesheets. These are essential to ensure your store looks and behaves as it should, but mismanaging them can also worsen your page load times. Besides the image SEO best practices we described in the section “High-quality images,” be sure to:
- Minify and compress your JavaScript and CSS to optimize their size.
- Load your assets at the right moment. An excellent example is photos of related products placed below the fold: you don’t need to load them immediately, slowing down the rendering of your pages. Instead, load and display them once the rest of the page has loaded, a technique called “lazy loading.” You can do the same with parts of your CSS and JS files: only immediately load what you need to display the page in the browser, then load the rest later.
3. Use browser caching: Most pages on your store rely on a shared set of assets, such as CSS stylesheets, Javascript code, and common images, such as your store’s logo. The problem is that browsers happily re-request any asset they encounter, meaning that when a visitor navigates from one page to another, their browser loads all the assets again. That’s such a waste!
Instead, your web server can signal to the browser to keep a cached copy of the assets and re-use them in the future. This is done by sending a cache header with the asset and instructing the browser to re-use the asset until a specific expiry time.
12. Highlight “You might also like” Products
Including related products is a great way to retain visitors who aren’t sure about their purchase yet by providing them with alternatives, and it’s also great for encouraging them to buy additional products.
For example, if you’re selling a hiking backpack that’s “reservoir compatible,” you could highlight reservoirs that go along with it.
From an SEO point of view, there’s a lot of value in including related products, too—these links strengthen your internal link structure and improve the other products’ SEO performance. When these products, in turn, link back, they “return the SEO favor.

13. Show Customer Reviews and Ratings
Another great way to improve the content and credibility of your product pages is by including customer reviews and ratings. These can provide valuable social proof and help to build trust with potential customers. They can also include additional keywords and phrases to improve your search engine ranking.
Product pages with customer reviews see conversion lifts of 52.2% more than their review-free counterparts, so this should be a no-brainer.
Genuine testimonials from customers who have tried your product speak volumes to in-market consumers trying to figure out whether or not to buy from you.
Letting customers share their experiences with your products and how they’ve helped solve problems is essential.
But there are other advantages, too.
Reviews help build trust – especially if you have an endorsement from a carefully vetted celebrity or famous influencer.
They also provide the fresh, unique content Google craves. Just be sure to mark them up with the review schema.
14. Apply Product Schema with Reviews
As we noted in the introduction, the battle for the click in search results is getting fiercer and fiercer. E-commerce businesses need to do whatever they can to stand out.
Always double-check that your Schema markup is correct before releasing it to production. You can do that using Google’s Rich Results Test.
15. Leverage Discontinued Products
Lots of stores don’t leverage the potential of discontinued products. These are products that are either temporarily or permanently unavailable. They may be out of stock, their product line may be discontinued, or maybe you stopped selling them.
Whatever the reason, handle them with care because these discontinued product pages often still carry a lot of value!
When we say “value,” we mean they either:
- are still getting (organic) traffic, or
- have links from other websites
If you expect a product to be in stock again later, keep it online and:
- Keep it in the XML sitemap and on-site search
- Put “out of stock” or a similar label on the product’s picture
- Hide the product’s price and keep visitors from adding it to the cart
- Show alternative products that are likely to fit the visitor’s needs
- Remove the Offer property from the Product Schema markup to prevent Schema penalties
- Let visitors know the product will be available again, or offer them a way to be notified once it’s back in stock
- Pause all active PPC campaigns directing customers to the product’s page

16. Include a FAQ or Q&A Section
If you want to go all out, you can even include FAQs about your selling products. You know your customers well, so you know what kinds of questions they’ll have. Covering these makes for more engaging and valuable content, and it will reduce support questions as well.
Alternatively, if you have an active community, you could include a moderated Q&A section on your product pages. This way, visitors can answer questions, and you will probably rank for even more queries visitors are searching for.
Whatever you decide, be sure to mark everything up with Schema. In the case of FAQs, use the FAQPage property. In the case of Q&As, use the Q&APage property. These will help you stand out even more!
17. Include Product Detail Pages in the XML Sitemap
Whether you publish new products or update existing ones, you want Google to crawl and (re)index them as soon as possible. That’s where XML sitemaps come in.
Create separate XML sitemaps for different content types. For example, create one each for category pages, product pages, manufacturers, supporting pages, and blog articles. Doing so makes tracking how Google indexes your indexing process easy if you’ve submitted your XML sitemaps in Google Search Console. Be sure only to include indexable pages that return the HTTP status 200 OK and limit the number of URLs per XML sitemap to 50,000.
18. Don’t Let Product Pages Become Orphans
With an extensive product inventory constantly changing, it’s easy to lose sight of products. Some product pages may become orphan pages when their parent category is removed.
Orphan pages aren’t a part of the site structure and thus have no internal links. Orphaned pages generally lead to lower rankings—and sometimes Google decides to de-index the products altogether.
Getting your product pages to rank with internal links is hard enough, so be on the lookout for this!
19. Monitor and Analyze Search Results
Once you have optimized your product pages, monitoring and analyzing their performance is essential. Analytics will help you understand what’s working and what’s not and allow you to improve your content and strategy.
Several tools are available to help you with this, such as Google Analytics and Ahrefs.
20. Use Schema Markup
One way to improve the visibility and performance of your product pages in search results is by using schema markup. Schema or Microdata markup is code you can add to your website to provide search engines with additional information about your products, such as their availability, price, and ratings.
This markup can help to enhance your search engine results and make them more attractive and informative to users.

Optimize Your E-Commerce Product Pages
Not optimizing your product pages means leaving money on the table. Likely a lot of it.
Start implementing the best practices we’ve described in this article. The best part is that they improve the user experience, too. After all, search engines have come so far that they now value the same things visitors do.
By following the steps outlined in this post, you can improve the SEO performance of your e-commerce product pages and drive more traffic and sales to your website.
Keyword research, unique and high-quality content, optimized page titles and meta descriptions, engaging images and videos, customer reviews, and ongoing analysis are critical elements of a successful SEO strategy for e-commerce product pages. We are here to help!

Are Your E-Commerce Product Pages Optimized?
Are you interested in increasing conversions and providing a better user experience? Our professional e-commerce designers will be happy to help you with this. But first, look at our portfolio and read our case studies.
Then, if you believe we are a good fit for your eCommerce web design needs, reach out to us! We offer a full range of consulting and design solutions for businesses and product brands.
And if you are unsure how to optimize your e-commerce product pages for better search rankings, let’s talk! We will listen to you, answer your questions, and help you attract, engage, and convert more online consumers!
Did You Optimize Your E-Commerce Product Pages?
Do you have anything to add to our tips for optimizing e-commerce product pages? Feel free to add your comments below so our audience can benefit and grab our feed so you don’t miss our next post! And feel free to share our post with your audience!
For more content relevant to your business or product brand – check out the range of articles on our web design blog. (This one, explaining how to write compelling product descriptions that sell, is an excellent place to start!)
Thank you! We appreciate your help ending bad business websites, one pixel at a time!
By Gregor Saita
Co-Founder / CXO
@gregorsaita

